Fennel; Foeniculum

This is about fennel's hormonal properties for breast enlargement. Properties are described, and there is information based on evidence on how to use fennel for breast enlargement.
Etymology
The genus of fennel goes by the scientific name of Foeniculum. The species Foeniculum vulgare goes by sweet fennel.
Fennel belongs to the Apiaceae family, otherwise known as the celery or carrot family.
The celery family includes several herbs: angelica (dong quai), anise, caraway, carrots, celery, coriander, cumin, dill, fennel and parsley.
Properties
Constituents of interest
Fennel contains diosgenin, anethole, estragole and dianethole. Diosgenin has progestogenic properties. Anethole, estragole and dianethole are anisoles.
Published studies
Fennel raises prolactin. Foeniculum use has had demonstrated a minor result of reducing body hair and for protecting ovarian tissue.
Anecdotal evidence
Use of fennel has caused menses to restart, so its use and amount should be very limited. The positive effects of fennel seem conditional when in the presence of bodily estrogen. Diosgenin or its metabolites behave as progestogenic.
Fennel has also caused brown spotting during menses which has been light and prolonged, which is likely due to its phytoprogestin content.
Use
Foeniculum for breast enhancement
Use of fennel should be limited to mid-proliferative phase or luteal phase to no more than 1 individual fennel seed at a time. Fennel should be avoided for those who have a history of hormonal imbalances. Use fennel with another primarily phyto-progestin.
Foeniculum or herbs with similar properties are in herb programs based on menstrual phases. There must be balance throughout phases, and combinations of herbs help the body acheive balance for health, breast growth and hip growth. It's important that menses is light and short. Also, preventing an excess of negative symptoms for menses helps set the balance for proliferative phase. Luteal phase uses a different combination of herbs than proliferative phase for symptoms. For a simplified herb schedule, where there's commonality of herb recommendations for symptoms such as swelling and signs of excess estrogen, use nonmenses. BCP01 is a composite page of pieces of different programs on birth control or IUD use.
Herb timing and combinations' success for breast enhancement relies on menstrual phases. Descriptions and pictures of results from herb combination use can be seen in programs. For more guidance, see guide, or hirsutism-topic.
Similar herbs
Wild yam (Dioscorea), saw palmetto, olive oil, prepared walnut and coconut are primarily progestins, which substitute or supplement fennel. These other herbs can be used in large amounts, because they don't contain anisoles which increase FSH, which is responsible for egg release. Wild yam and fennel contain the phyto-progestin diosgenin.
Angelica (dong quai), anise, caraway, carrots, celery, coriander, cumin, dill, fennel and parsley within the celery family have varying hormonal properties aside from many of them containing anisoles. Anise, dill and liquorice definitely contain anethole, estragole or related compounds.
Spearmint, peppermint and basil contain anisole constituents: anethole, estragole or similar phytochemicals. It seems basil is more androgenic, while spearmint and peppermint usually have estrogenic actions. Spearmint and peppermint have been replaced in other herb profiles.
Precautions
While fennel is a common spice used in cooking, there are questions about its and other spices within the celery family's role in cancer. There role of anisoles including anethole and estragole within related spices on cancer is unclear. Many herbs within the carrot family related to fennel have these anisoles.
Unfortunately, the celery family has a few toxic members that can cause severe permanent injury to the touch and/or death if ingested: hemlock, fool's parsley and hog weed. These deadly plants resemble other members within the celery family.
Be sure you properly identify safe herbs before handling or use.
See precautions for more details of care to be taken with herb use. Proper nutrition is a consideration for health. Also, check for the latest blog updates about herb and hormone safety.
It is very important that menses be light and not prolonged.
If you have hirsutism, PCOS, hot-flashes, other signs of hormone imbalances, see estrogen-imbalance, and hirsutism program journals at hirusitism-topic before trying herbs.
Herb concentrates can be tens of times more potent by weight than herbs in solid form. This can easily lead to hormone imbalances. For this reason, concentrate extracts are not recommended for extended or excessive internal use, especially during fertility years. Concentrates shouldn't be used to overcome plateaus. Another issue with herbal extracts, is that they may not have the full range of properties of the herb. Essential oils are not recommended for breast enhancement. If opting to use herbal extracts, use food grade extracts, with no more than 1 drop at a time diluted in water.
More
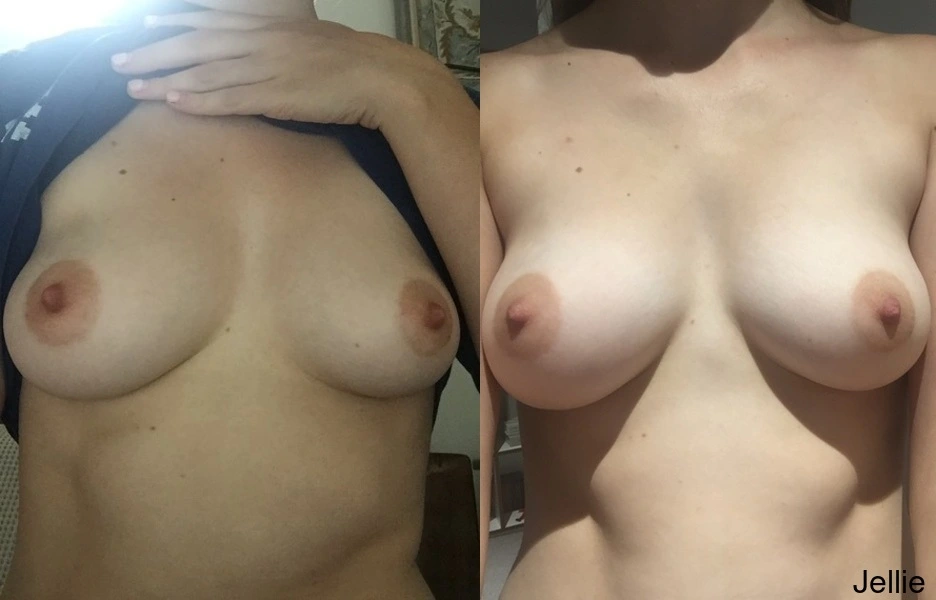
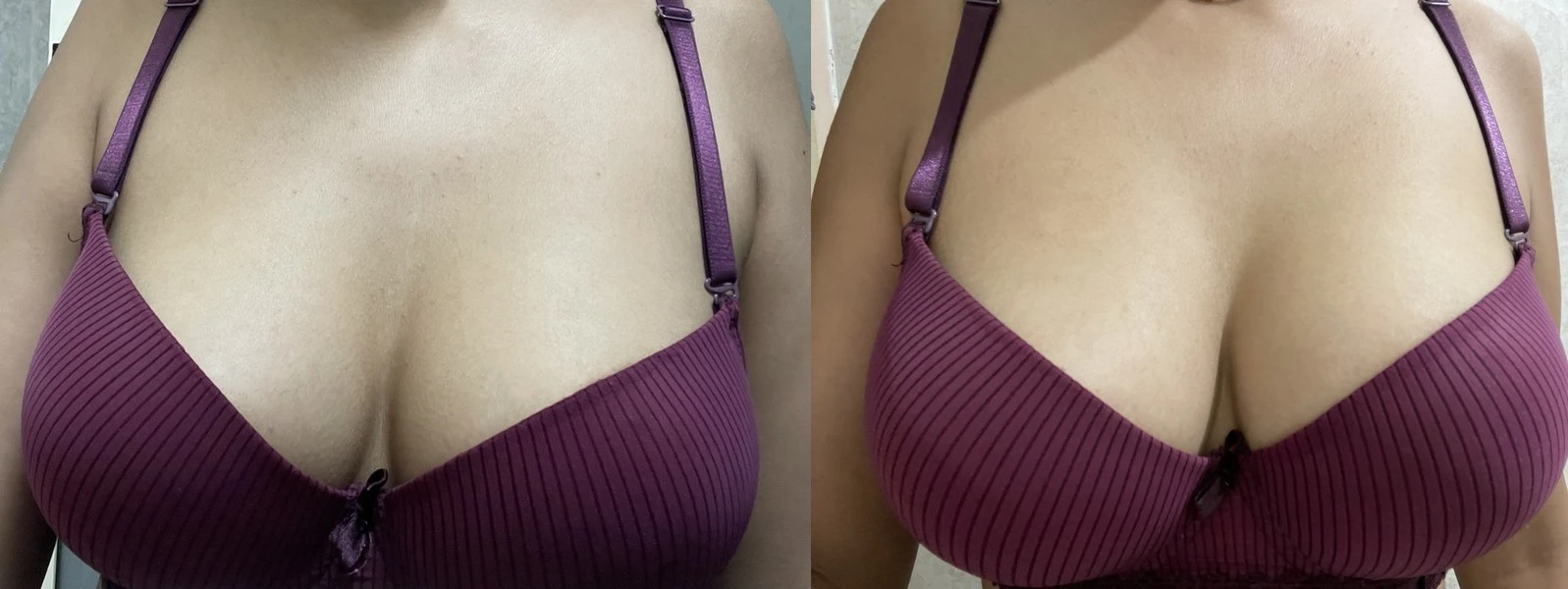

For the latest herb programs and how to get started, see: guide. Pictures of breast enhancement can be seen in the program journals of Anon02, Anon08, Anon09, Bubblemelon and Jellie.
For resources on hips and butt enhancement, see: /appendix/hips-butt-enhancement and /appendix/kettlebell.
breast-endocrinology.pdf describes the science of breast development and endocrinology. It also describes symptoms related to hormone imbalances. Biology and hormone imbalances are excerpts from this ebook. breast-endocrinology.pdf uses a Creative Commons (CC BY-ND 4.0) license.
Breast.is blog
References:
- The effect of fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) gel 3% in decreasing hair thickness in idiopathic mild to moderate hirsutism, A randomized placebo controlled clinical trial.. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3894467/.
- Study of Foeniculum vulgare Effect on Folliculogenesis in Female Mice. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4122825/.
- Foeniculum vulgare Mill: A Review of Its Botany, Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Contemporary Application, and Toxicology. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4137549/.
- Effect of Foeniculum vulgare (fennel) vaginal cream on vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women: A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26617271.
- Fennel and anise as estrogenic agents. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/6999244.
- A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of fennel (foeniculum vulgare) on menopausal symptoms: a high placebo response. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29755029/.
- Effect of fennel vaginal cream on sexual function in postmenopausal women: a double blind randomized controlled trial. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29696061/.
- Ovarian protection in cyclophosphamide-treated mice by fennel. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28959636/.
- Effect of fennel on pain intensity in dysmenorrhoea: A placebo-controlled trial. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23559811/.
- Oral fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) drop effect on primary dysmenorrhea: Effectiveness of herbal drug. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23983742/.
- EFFECT OF FOENICULUM VULGARE SEED EXTRACT ON MAMMARY GLANDS AND OVIDUCTS OF OVARIECTOMISED RATS. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22557513/.
- Effect of the aqueous extract of Foeniculum vulgare (fennel) on the kidney in experimental PCOS female rats. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25050308/.
- Effect of Foeniculum vulgare Mill. (fennel) on menopausal symptoms in postmenopausal women: a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled trial.. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28509813/.
- Rescue effects of aqueous seed extracts of Foeniculum vulgare and Carum carvi against cadmium-induced hepatic, renal and gonadal damage in female albino rats. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29268967/.
- Thresholds of carcinogenicity of flavors. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12151622.
Etymology & Definitions:
- USDA Plant classification: fennel. https://plants.usda.gov/java/ClassificationServlet?source=profile&symbol=FOENI&display=31.
- USDA Plant classification: sweet fennel. https://plants.usda.gov/java/ClassificationServlet?source=display&classid=FOVU.
- The Plant List: Foeniculum. http://www.theplantlist.org/1.1/browse/A/Apiaceae/Foeniculum/.
Resources:
- Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed) [Internet]: Fennel. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK501793/.
