Black Cohosh

This is about black cohosh, including its hormonal properties and potential use for breast enhancement. Black cohosh has a reputation for lowering hot-flashes.
Etymology
Black cohosh belongs to the genus of Actaea, formerly Cimicifuga. It is known as baneberry, black snakeroot, bug root and bugbane
Black cohosh belongs to the Ranunculaceae or Buttercup family.
Properties
Studies have shown black cohosh to reduce hot flashes.
Black cohosh lowers LH possibly circumstantially, but it has no immediate effects on FSH or estrogen levels. Many of Cimicifuga's hormonal effects are a result of its phytohormones binding to ERα in the pituitary gland. Black cohosh raises progestogens, perhaps limited to late secretory phase.
Use
Actaea for breast enhancement
Black cohosh should be avoided during menses, proliferative, ovulation and premenstrual phases. This herb would likely cause breast shrinking and estrogen desensitization if used during proliferative. It could cause growth during premenstrual and menses, but it is likely the wrong herb to use here for continued reproductive health.
Black cohosh can likely be used scarcely during mid-secretory (within luteal) phase. Actaea is not exactly like hops, so it cannot be used in all circumstances that hops is used. Hops lowers both FSH and LH, while black cohosh only lowers LH. The full hormonal implications of this for black cohosh are not clear. If black cohosh were to be used, it should be limited to under 100mg at a time. Actaea likely should be avoided when there's swelling or bloating.
Actaea or herbs with similar properties are in herb programs based on menstrual phases. There must be balance throughout phases, and combinations of herbs help the body acheive balance for health, breast growth and hip growth. It's important that menses is light and short. Also, preventing an excess of negative symptoms for menses helps set the balance for proliferative phase. Luteal phase uses a different combination of herbs than proliferative phase for symptoms. For a simplified herb schedule, where there's commonality of herb recommendations for symptoms such as swelling and signs of excess estrogen, use nonmenses. BCP01 is a composite page of pieces of different programs on birth control or IUD use.
Herb timing and combinations' success for breast enhancement relies on menstrual phases. Descriptions and pictures of results from herb combination use can be seen in programs. For more guidance, see guide, or hirsutism-topic.
Similar herbs
Herbs with similar properites with possibly the same mechanism for action to black cohosh include, hops (Humulus) and milk thistle (Silybum).
Evening primrose is used to allevate hot-flashes, but it has a different mechanism for action and its use is now discouraged for NBE due to it increasing FSH.
Precautions
Overuse of Black cohosh can cause symptoms such as headaches, which is likely due to increases in estrogen. It is likely that black cohosh contributes to liver damage, as there are indications of this. Opt for hops instead.
See precautions for more details of care to be taken with herb use. Proper nutrition is a consideration for health. Also, check for the latest blog updates about herb and hormone safety.
It is very important that menses be light and not prolonged.
If you have hirsutism, PCOS, hot-flashes, other signs of hormone imbalances, see estrogen-imbalance, and hirsutism program journals at hirusitism-topic before trying herbs.
Herb concentrates can be tens of times more potent by weight than herbs in solid form. This can easily lead to hormone imbalances. For this reason, concentrate extracts are not recommended for extended or excessive internal use, especially during fertility years. Concentrates shouldn't be used to overcome plateaus. Another issue with herbal extracts, is that they may not have the full range of properties of the herb. Essential oils are not recommended for breast enhancement. If opting to use herbal extracts, use food grade extracts, with no more than 1 drop at a time diluted in water.
More
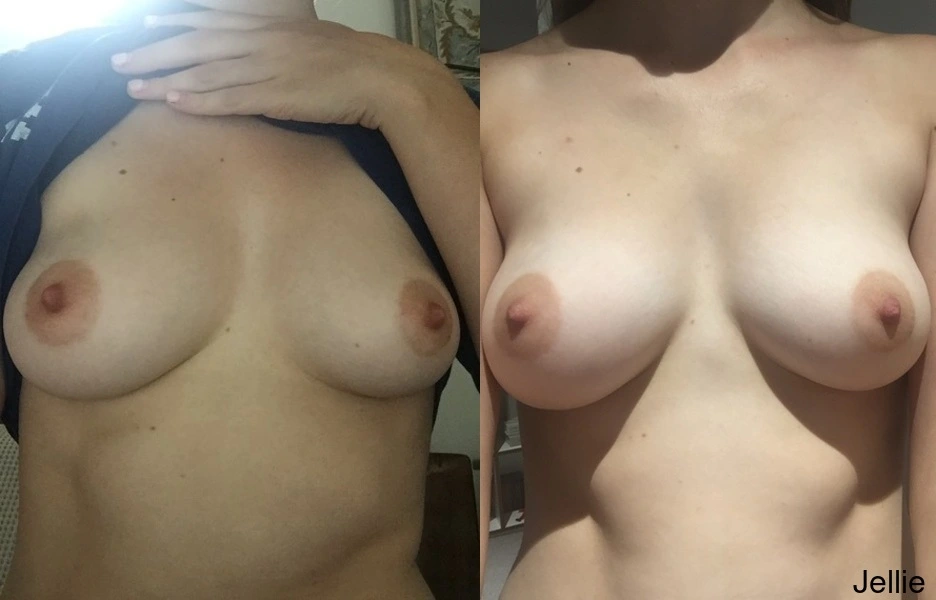

For the latest herb programs and how to get started, see: guide. Pictures of breast enhancement can be seen in the program journals of Anon02, Anon08, Anon09, Bubblemelon and Jellie.
For resources on hips and butt enhancement, see: /appendix/hips-butt-enhancement and /appendix/kettlebell.
breast-endocrinology.pdf describes the science of breast development and endocrinology. It also describes symptoms related to hormone imbalances. Biology and hormone imbalances are excerpts from this ebook. breast-endocrinology.pdf uses a Creative Commons (CC BY-ND 4.0) license.
Breast.is blog
References:
- A review of effective herbal medicines in controlling menopausal symptoms. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5783135/.
- Effects of extracts from Cimicifuga racemosa on gonadotropin release in menopausal women and ovariectomized rats.. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1798794.
- Herbal medicine for the management of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and associated oligo/amenorrhoea and hyperandrogenism; a review of the laboratory evidence for effects with corroborative clinical findings. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4528347/.
- A comparative study on the effect of “black cohosh” and “evening primrose oil” on menopausal hot flashes. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5868221/.
- Black Cohosh (Actaea Racemosa, Black Bugbane, Black Snakeroot, Fairy Candle). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29261886.
Etymology & Definitions:
- University of Vermont: Cimicifuga. http://pss.uvm.edu/pss123/percimic.html.
Resources:
- NIH: Black Cohosh. https://nccih.nih.gov/health/blackcohosh/ataglance.htm.
